-
SQL Installing SSMS
-
SQL Syntax
-
SQL Datatype
-
SQL Database
-
SQL Table
-
SQL Select
-
SQL Distinct
-
SQL Count
-
SQL Top
-
SQL Aliases
-
SQL In
-
SQL Insert
-
SQL Update
-
SQL Null
-
SQL Like
-
SQL Wildcards
-
SQL Nested Query
-
SQL Between
-
SQL Unique
-
SQL Primary Key
-
SQL Foreign Key
-
SQL Check
-
SQL Default
-
SQL Database Diagram
-
SQL Stored Procedures
-
SQL Joins
-
SQL Inner Join
-
SQL Left Join
-
SQL Right Join
-
SQL Full Join
-
SQL Trigger
SQL Select Aliases
An alias is created with the AS keyword. SQL ‘AS’ is used to assign a new name temporarily to a table column or even a table. It makes an easy presentation of query results and allows the developer to label results more accurately without permanently renaming table columns or even the table itself.
Example:
SELECT Column_Name1 AS New_Column_Name, Column_Name2 As New_Column_Name FROM Table_Name;
Here, the Column_Name is the name of a column in the original table, and the New_Column_Name is the name assigned to a particular column only for that specific query. This means that New_Column_Name is a temporary name that will be assigned to a query.
Let us take a table named orders, and it contains the following data:
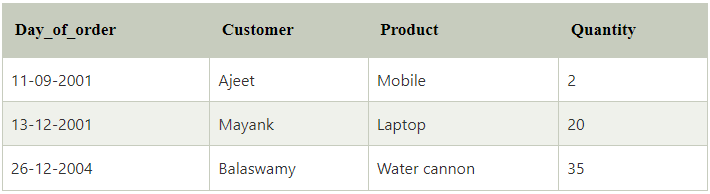
Suppose you want to rename the ‘day_of_order’ column and the ‘customer’ column as ‘Date’ and ‘Client’, respectively.
SELECT day_of_order AS ‘Date’, Customer As ‘Client’, Product, Quantity FROM orders;
The result will be shown as this table:
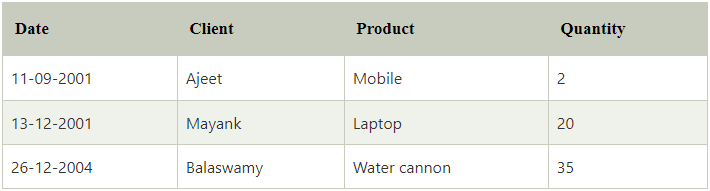
From the above results, we can see that temporarily the ‘Day_of_order’ is renamed as ‘date’ and ‘customer’ is renamed as ‘client’.
Consider we have a student table with the following data.

Suppose you want a student name and the average of the percentage of the student under the temporary column name ‘Student’ and ‘Student_Percentage’, respectively.
SELECT Student_Name AS Student, AVG (Student_Percentage) AS Average_Percentage FROM students;
Here, to calculate the average, we have used AVG () function. Further, the calculated average value of the percentage will be stored under the temporary name ‘Average_Percentage’.
The result will be shown as this table:

Assigning a temporary name to a table
Instead of remembering the table names, we can create an alias for them. We can assign a temporary name to the columns of a table; similarly, we can create an alias for a table.
Let’s understand it with the help of an example.
Write a query to create an alias of a table named ‘students’.
SELECT s.Student_RollNo, s.Student_Name, s.Student_Gender, s.Student_PhoneNumber, s.Student_HomeTown FROM students AS s WHERE s.Student_RollNo = 3;
The result will be shown as this table:

Course Video
NOTE: Practice below questions on site editor.
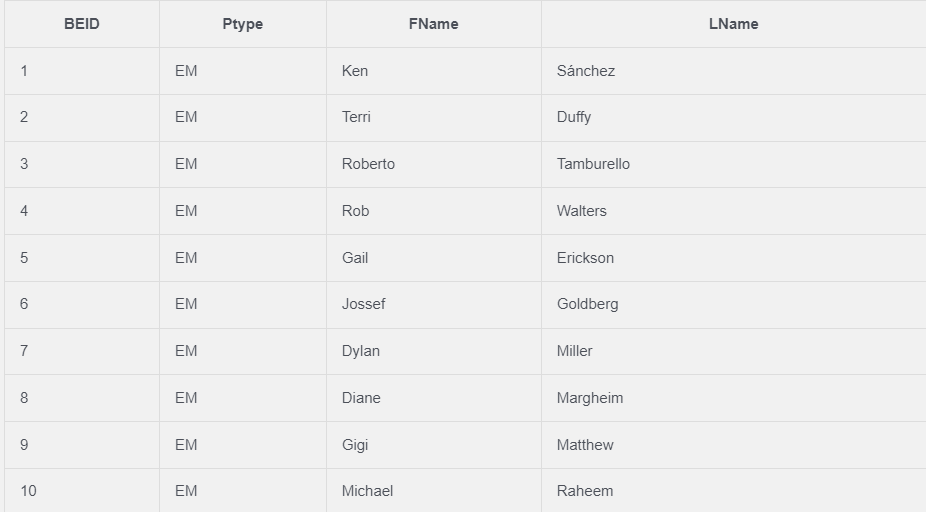
1. Write a SQL Query get BusinessEntityID as BEID, PersonType as Ptype, FirstName as FName, LastName as LName from Person_Person table.
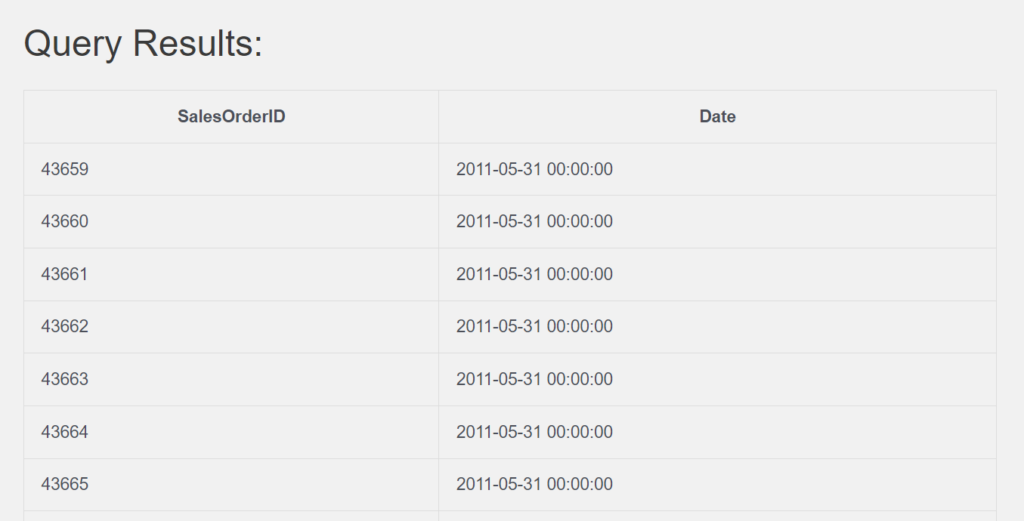
2. Retrieve the salesOrderID and OrderDate from the Sales_SalesOrderHeader table and display OrderDate as Date.
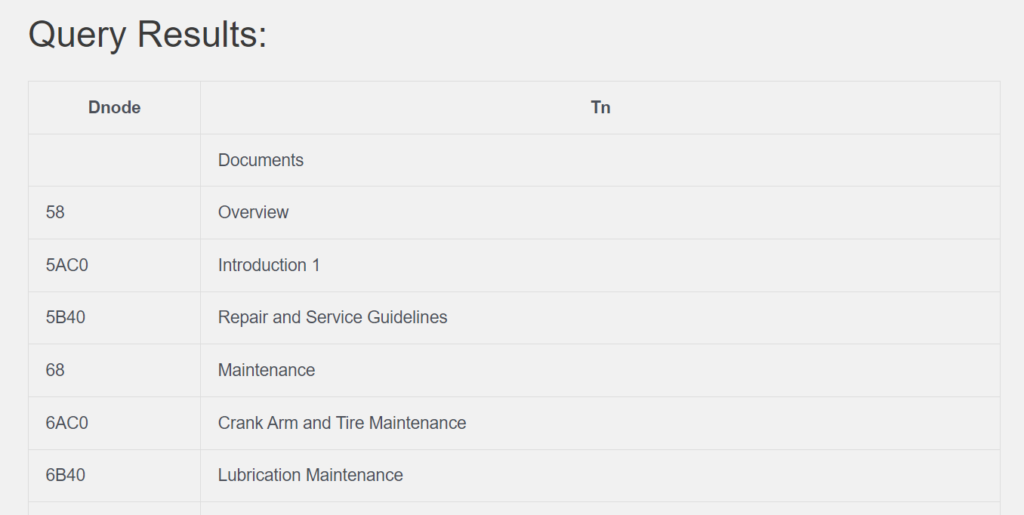
3. Write a SQL Query Retrieve DocumentNode as Dnode , Title as Tn from Production_Document.
(13 row count)
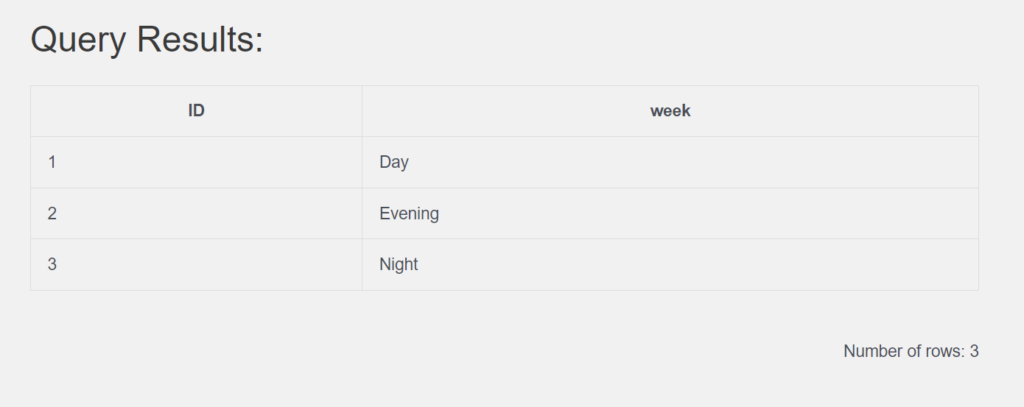
4. Retrieve shiftID as ID , Name as week from HumanResources_Shift table
(3 row count)
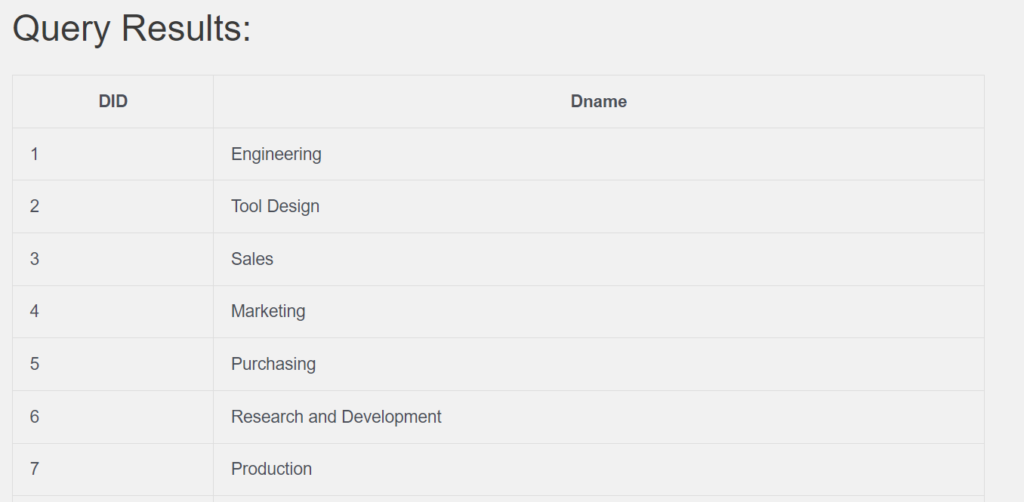
5. Retrieve the departmentID as DID, Name as DName from HumanResources_Department.
(16 row count)

YouTube Reference :
1) SQL Select Aliases in Hindi/Urdu
2) SQL Select Aliases in English


