-
SQL Installing SSMS
-
SQL Syntax
-
SQL Datatype
-
SQL Database
-
SQL Table
-
SQL Select
-
SQL Distinct
-
SQL Count
-
SQL Top
-
SQL Aliases
-
SQL In
-
SQL Insert
-
SQL Update
-
SQL Null
-
SQL Like
-
SQL Wildcards
-
SQL Nested Query
-
SQL Between
-
SQL Unique
-
SQL Primary Key
-
SQL Foreign Key
-
SQL Check
-
SQL Default
-
SQL Database Diagram
-
SQL Stored Procedures
-
SQL Joins
-
SQL Inner Join
-
SQL Left Join
-
SQL Right Join
-
SQL Full Join
-
SQL Trigger
SQL Comments
A comment is a programmer-readable explanation or annotation used in the SQL statements that do not affect their execution. It is used to make SQL statements easier to understand for humans. We can include the comment in between any keywords, parameters, or punctuation marks in a statement. During the parsing of SQL code, the SQL Server engine usually ignores them. It matters a lot in SQL queries like programming languages.
Some examples of using comments are:
– It can be used to label a section of code to make it easier to understand for others.
– It also allows us to modify things later when we remove a column shown in the output of a SELECT statement but still keep the name in the query.
– To check data and performance, disable lines of a WHERE clause.
SQL Server provides three types of comments, which are given below:
1. single-line Line Comment
2. Multiline Comment
Single-Line Comments
Comments are mostly used to document the code and provide descriptions of what it does. Let us describe each type of comment in detail with examples.
A comment that starts and ends in a single line is known as a single-line comment. We can add comments with the same SQL statement, nested at the end of the SQL statement or on a separate line. The SQL Server engine does not evaluate the comments. Single line comments are represented by the double dash (- -) symbol.
We can use the single-line comment as below:
— the text of comment written here
Example:
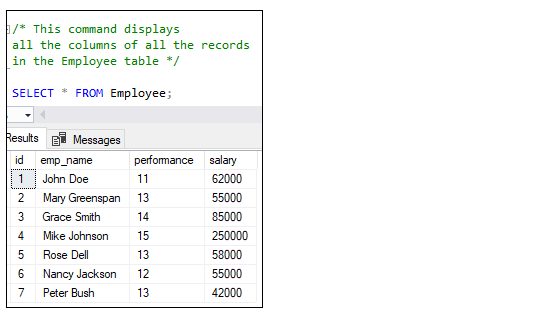
The following statement is executed correctly and displayed the employee details:
— This command displays employee information
SELECT * FROM Employee;
Executing the statement will give the below output without parsing comment:
Course Video
NOTE: Practice below practice questions on MSSQL SERVER, it will not execute on site editor.
1. Write a single line comment to describe the purpose of the following SQL query:

2. Write a multi-line comment to describe the purpose of the following SQL query:
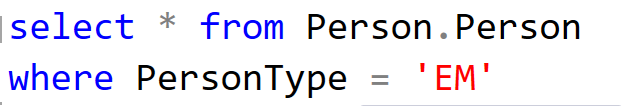
3. In below query Comment FirstName column in the query :