-
JS Setting Up Environment
-
JS Syntax
-
JS Comments
-
JS Generating OutPut
-
JS Variables
-
JS Data Types
-
JS String
-
JS String Methods & Properties
-
JS Template Literals
-
JS Operators
-
JS Conditional Statements
-
JS Break and Continue
-
JS Functions
-
JS DOM
-
JS DOM Methods and Elements
-
JS DOM HTML/CSS Manipulation
-
JS DOM Navigation & Nodes
-
JS Events
-
JS Array
-
JS Loops
-
JS Object
-
JS Accessors
-
JS Object Constructors
-
JS Prototype & Iterables
-
JS Date & Time Function
-
JS Math Function
-
JS Storage
-
JS Classes
-
JS Map & Set
-
JS Global Scope
-
JS Rest and Spread
-
JS Error Handling
-
JS Asynchronous
-
JS Promise
-
JS Async/Await
-
JS Node.js
-
JS Regular Expression
-
JS Fetch API
-
JS BOM
-
JS Form Validation
-
JS Practiced Example
-
JS Projects
DOM Methods and Elements
DOM (Document Object Model) methods and elements are essential components in web development, enabling developers to interact with and manipulate the content of an HTML document using JavaScript.
DOM Methods
DOM methods are functions provided by the DOM API that allow developers to perform various actions on the HTML document.
| Method | Description | Example |
| getElementById() | Returns the element with the specified ID | const element = document.getElementById(‘example’); |
| getElementsByClassName() | Returns a collection of elements with the specified class name | const elements = document.getElementsByClassName(‘example’); |
| getElementsByTagName() | Returns a collection of elements with the specified tag name | const elements = document.getElementsByTagName(‘p’); |
| querySelector() | Returns the first element that matches a CSS selector | const element = document.querySelector(‘#example .child-element’); |
| querySelectorAll() | Returns a collection of elements that match a CSS selector | const elements = document.querySelectorAll(‘p.example’); |
DOM Elements
JavaScript is most commonly used to get or modify the content or value of the HTML elements on the page, as well as to apply some effects like show, hide, animations etc
Element | Description | Example |
innerHTML | Gets or sets the HTML content of an element | document.getElementById(‘myDiv’).innerHTML = ‘<strong>Hello World!</strong>’; |
textContent | Gets or sets the text content of an element | document.getElementById(‘myDiv’).textContent = ‘Hello World!’; |
createElement(tagName) | Creates a new HTML element with the specified tag name | var newDiv = document.createElement(‘div’); |
createTextNode(text) | Creates a new text node with the specified text | var newText = document.createTextNode(‘Hello World!’); |
appendChild(newNode) | Adds a new child node to the end of an element’s children | document.getElementById(‘myDiv’).appendChild(newDiv); |
insertBefore(newNode, referenceNode) | Inserts a new child node before a reference node | document.getElementById(‘myDiv’).insertBefore(newDiv, referenceDiv); |
Course Video
YouTube Reference :
1) JavaScript DOM Targeting Methods Tutorial in Hindi / Urdu
2) JavaScript DOM Get & Set Value Methods Tutorial in Hindi / Urdu
3) JavaScript DOM querySelector & querySelectorAll Tutorial in Hindi
4) JavaScript DOM Tutorial – Get Element By ID in English
5) JavaScript DOM Tutorial – Get Elements By Class or Tag in English
6) JavaScript DOM Tutorial – The Query Selector in English
Examples for Practice
You have to solve all the questions given below in the editor without copy-pasting.
1. Write a JS program in which Change the Background color of a Paragraph using the DOM element.
The task is to write a JavaScript program that changes the background color of a paragraph using the Document Object Model (DOM).
1. Access the Paragraph Element: Use JavaScript to select the paragraph element in the HTML document. You can do this by using document.getElementById(), document.querySelector(), or other similar methods to select the paragraph element by its ID or class.
2. Change the Background Color: Once you have selected the paragraph element, use the .style.backgroundColor property to change its background color. You can set this property to any valid CSS color value, such as “red”, “blue”, “#00ff00”, etc.
Here’s an example program:
<body>
<p id=”myParagraph”>This is a paragraph.</p>
<script>
// Access the paragraph element using its ID
var paragraph = document.getElementById(“myParagraph”);
// Change the background color of the paragraph
paragraph.style.backgroundColor = “yellow”;
</script>
</body>
Output

2. Write a JS program to change the border style of the Paragraph by taking the border type from User (Dotted, Solid, Dashed) and changing the style using the DOM element.
The task is to write a JavaScript program that allows the user to input a border style (Dotted, Solid, Dashed) and changes the border style of a paragraph using the Document Object Model (DOM).
1. Get User Input: Use the prompt function to ask the user to enter a border style. Store the user input in a variable.
2. Access the Paragraph Element: Use JavaScript to select the paragraph element in the HTML document. You can do this by using document.getElementById(), document.querySelector(), or similar methods.
3. Change the Border Style: Once you have selected the paragraph element, use the .style.borderStyle property to change its border style. Set this property to the user input received from the prompt.
Here’s an example program:
<body>
<p id=”myParagraph”>This is a paragraph.</p>
<script>
// Access the paragraph element using its ID
var paragraph = document.getElementById(“myParagraph”);
// Get user input for border style
var userBorderStyle = prompt(“Enter border style (Dotted, Solid, Dashed):”);
// Change the border style of the paragraph based on user input
paragraph.style.borderStyle = userBorderStyle;
</script>
</body>
Output
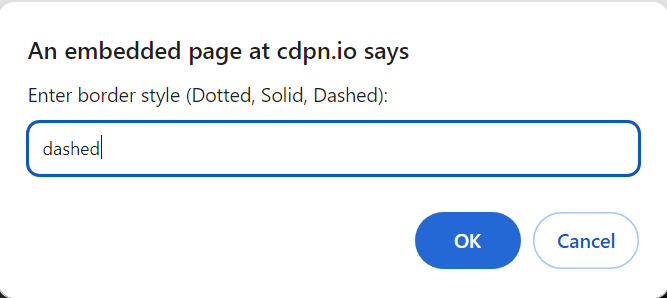

3. Using JS DOM elements change the color of the Paragraph as follows:-
Paragraph 1:- Red
Paragraph 2:- Blue
Paragraph 3:- Green
The task is to write a JavaScript program that changes the color of three paragraphs with specific colors using the Document Object Model (DOM).
1. Access Paragraph Elements: Use JavaScript to select the three paragraph elements in the HTML document. You can do this by using document.getElementById(), document.querySelector(), or similar methods for each paragraph.
2. Change the Color: Once you have selected each paragraph element, use the .style.color property to change its text color. Set this property to the specific color for each paragraph.
Here’s an example program:
<body>
<p id=”paragraph1″>Paragraph 1: This is red.</p>
<p id=”paragraph2″>Paragraph 2: This is blue.</p>
<p id=”paragraph3″>Paragraph 3: This is green.</p>
<script>
// Access paragraph elements using their IDs
var paragraph1 = document.getElementById(“paragraph1”);
var paragraph2 = document.getElementById(“paragraph2”);
var paragraph3 = document.getElementById(“paragraph3”);
// Change the color of each paragraph
paragraph1.style.color = “red”;
paragraph2.style.color = “blue”;
paragraph3.style.color = “green”;
</script>
</body>
Output

4. Write a JS program to change the color and Background of the Paragraph by taking the color and backgroundcolor name from the User and changing the style of the Paragraph using a DOM element.
The task is to write a JavaScript program that allows the user to input both the text color and background color and then changes the style of a paragraph using the Document Object Model (DOM).
1. Get User Input: Use the prompt function to ask the user to enter the text color and background color. Store these inputs in separate variables.
2. Access the Paragraph Element: Use JavaScript to select the paragraph element in the HTML document. You can do this by using document.getElementById(), document.querySelector(), or similar methods.
3. Change the Style: Once you have selected the paragraph element, use the .style.color property to change its text color, and the .style.backgroundColor property to change its background color. Set these properties to the user inputs received from the prompt.
Here’s an example program:
<body>
<p id=”myParagraph”>This is a paragraph with dynamic style.</p>
<script>
// Access the paragraph element using its ID
var paragraph = document.getElementById(“myParagraph”);
// Get user input for text color and background color
var userTextColor = prompt(“Enter text color:”);
var userBackgroundColor = prompt(“Enter background color:”);
// Change the style of the paragraph based on user input
paragraph.style.color = userTextColor;
paragraph.style.backgroundColor = userBackgroundColor;
</script>
</body>
Output
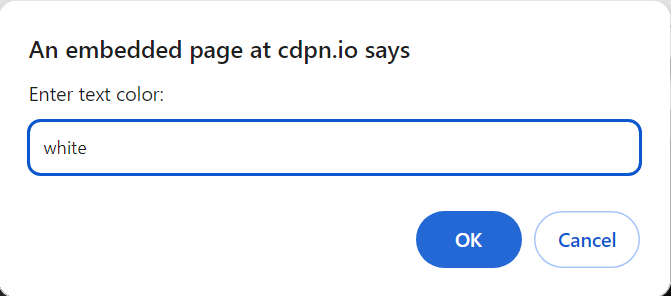
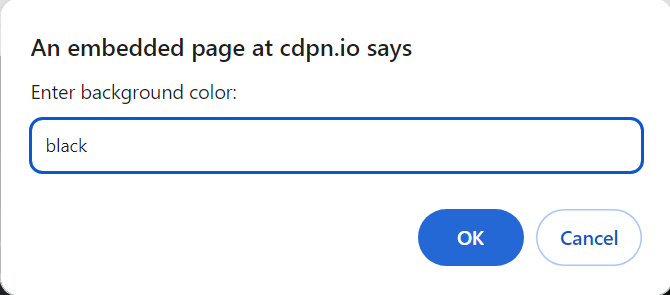

5. Design a program that takes user input and uses a function to check if the answer is correct. If the answer is correct, display a success message with the class adding success; if it’s wrong, display an error message with the class adding error. Must color change Classes :
Success [Color: green), Error {color: red}
The task is to write a JavaScript program that takes user input, checks if the answer is correct using a function, and displays a success or error message with corresponding color changes.
1. Get User Input: – Use the prompt function to ask the user to enter their answer. Store the user input in a variable.
2. Define the Check Answer Function:
– Create a function called checkAnswer that takes the user’s input as a parameter.
– Inside this function, check if the answer is correct.
3. Display Success or Error Message:
– Use the Document Object Model (DOM) to display a message on the HTML document.
– If the answer is correct, add the class “success” with the text color set to green.
– If the answer is wrong, add the class “error” with the text color set to red.
Here’s an example program:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<style>
.success {
color: green;
}
.error {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id=”resultMessage”></div>
<script>
// Define the checkAnswer function
function checkAnswer(userInput) {
var correctAnswer = “9”;
// Convert both answers to uppercase for case-insensitive comparison
userInput = userInput.toUpperCase();
correctAnswer = correctAnswer.toUpperCase();
// Check if the answer is correct
if (userInput === correctAnswer) {
displayMessage(“Success! You got it right.”, “success”);
} else {
displayMessage(“Error! Wrong answer.”, “error”);
}
}
// Define a function to display the message with the specified class
function displayMessage(message, className) {
var resultMessage = document.getElementById(“resultMessage”);
resultMessage.textContent = message;
resultMessage.className = className;
}
// Wrap the code in a window load event
window.onload = function() {
// Get user input for the answer
var userAnswer = prompt(“5 + 4 = ?”);
// Call the checkAnswer function with user input
checkAnswer(userAnswer);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
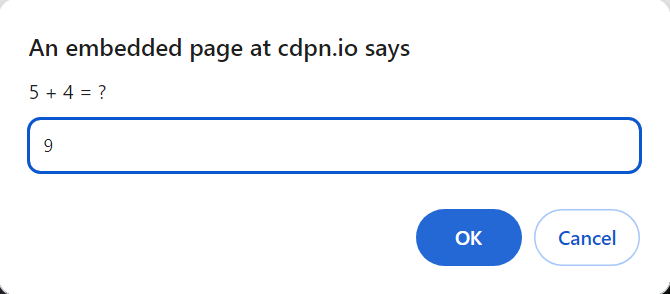

6. Create a JavaScript program that includes an HTML element with a question and multiple-choice answers. Get the answer from the user by prompt. When the user selects the wrong answer, change the color of the text to red. If correct change the color Green. For Example:
2+2=?
The answer is 6
The answer is 9
The answer is 4
The task is to write a JavaScript program that includes an HTML element with a question and multiple-choice answers. When the user selects the wrong answer, the text color should change to red, and if the answer is correct, the text color should change to green.
1. Get User Input: Use the prompt function to ask the user to select an answer from the multiple-choice options. Store the user input in a variable.
2. Check Answer and Change Text Color:
– Use JavaScript to check if the user’s answer is correct.
– If the answer is correct, change the text color to green.
– If the answer is wrong, change the text color to red.
Here’s an example program:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
.correct {
color: green;
}
.wrong {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id=”question”>
<p>2 + 2 = ?</p>
<ul>
<li onclick=”checkAnswer(6)”>The answer is 6</li>
<li onclick=”checkAnswer(9)”>The answer is 9</li>
<li onclick=”checkAnswer(4)”>The answer is 4</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
// Function to check the user’s answer
function checkAnswer(userAnswer) {
var correctAnswer = 4;
// Check if the answer is correct
if (userAnswer === correctAnswer) {
displayResult(“Correct! Well done.”, “correct”);
} else {
displayResult(“Wrong answer. Try again.”, “wrong”);
}
}
// Function to display the result with the specified class
function displayResult(message, className) {
var resultElement = document.getElementById(“question”);
resultElement.innerHTML = ‘<p>’ + message + ‘</p>’;
resultElement.className = className;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output




