-
JS Setting Up Environment
-
JS Syntax
-
JS Comments
-
JS Generating OutPut
-
JS Variables
-
JS Data Types
-
JS String
-
JS String Methods & Properties
-
JS Template Literals
-
JS Operators
-
JS Conditional Statements
-
JS Break and Continue
-
JS Functions
-
JS DOM
-
JS DOM Methods and Elements
-
JS DOM HTML/CSS Manipulation
-
JS DOM Navigation & Nodes
-
JS Events
-
JS Array
-
JS Loops
-
JS Object
-
JS Accessors
-
JS Object Constructors
-
JS Prototype & Iterables
-
JS Date & Time Function
-
JS Math Function
-
JS Storage
-
JS Classes
-
JS Map & Set
-
JS Global Scope
-
JS Rest and Spread
-
JS Error Handling
-
JS Asynchronous
-
JS Promise
-
JS Async/Await
-
JS Node.js
-
JS Regular Expression
-
JS Fetch API
-
JS BOM
-
JS Form Validation
-
JS Practiced Example
-
JS Projects
Object Constructors
In JavaScript, a constructor function is a special type of function used for creating and initializing objects. Constructor functions are typically used with the new keyword to instantiate objects based on a blueprint defined by the constructor.
Here’s an overview of how constructor functions work:
Creating a Constructor Function:
A constructor function is defined like any other function, but it’s conventionally named with an initial uppercase letter to distinguish it from regular functions.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
In this example, we’ve created a Person constructor function that takes name and age parameters and sets them as properties of the object being created.
Instantiating Objects with new:
To create an instance (object) of the constructor function, you use the new keyword.
const john = new Person(“John”, 30);
To create an instance (object) of the constructor function, you use the new keyword.
Using this Keyword:
Inside the constructor function, the this keyword refers to the newly created object. It’s used to set properties on that object.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
In this example, this.name and this.age refer to properties of the object being created.
Adding Methods to a Constructor:
You can also add methods to the constructor function, which will be shared by all instances created using that constructor.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayHello = function() {
console.log(“Hello, my name is ” + this.name);
};
}
Now, each Person object created using this constructor will have a sayHello method.
Using Constructor Objects:
Once an object is created using a constructor, you can access its properties and methods.
console.log(john.name); // Output: John
console.log(john.age); // Output: 30
john.sayHello(); // Output: Hello, my name is John
Benefits of Constructor Functions:
1. Code Reusability: Constructor functions allow you to define a blueprint for objects, making it easy to create multiple instances with similar properties and methods.
2. Encapsulation: Properties and methods are encapsulated within the object, providing a way to organize and structure your code.
3. Shared Methods: Methods defined in the constructor are shared among all instances, optimizing memory usage.
Constructor functions are a fundamental part of object-oriented programming in JavaScript and are widely used to create and manage objects in a structured manner.
Course Video
YouTube Reference :
1) JavaScript Tutorial in Hindi for Beginners – Object constructor function in JavaScript
2) Advance Javascript – OOP Introduction Tutorial in Hindi / Urdu
3) JavaScript Tutorial in Hindi for Beginners – The JavaScript “this” Keyword
4) JavaScript Object Methods And This Keyword In JavaScript | Tutorial For Beginners in English
5) JavaScript Object Constructors | JavaScript Constructor Function in English
Examples for Practice
You have to solve all the questions given below in the editor without copy-pasting.
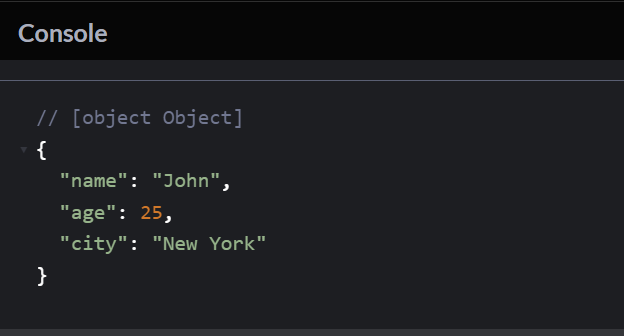
1. Create an object named person with properties name, age, and city. Set appropriate values and log the entire object to the console.
Here’s an example program:
let person = {
name: “John”,
age: 25,
city: “New York”
};
console.log(person);
Output
2. Add a new property occupation to the person object from Example 1 and set its value to “Engineer”. Log the updated object to the console.
Here’s an example program:
let person = {
name: “John”,
age: 25,
city: “New York”
};
person.occupation = “Engineer”;
console.log(person);
Output

3. Create a function printInfo that takes a person object as a parameter and logs a message like “John is 25 years old and lives in New York.” using the object properties.
Here’s an example program:
let person = {
name: “John”,
age: 25,
city: “New York”
};
function printInfo(person) {
console.log(`${person.name} is ${person.age} years old and lives in ${person.city}.`);
}
printInfo(person);
Output

4. Create an object named car with properties make, model, and year. Write a function displayCarInfo that takes a car object as a parameter and logs a message like “The car is a Toyota Camry from 2020.”
Here’s an example program:
let car = {
make: “Toyota”,
model: “Camry”,
year: 2020
};
function displayCarInfo(car) {
console.log(`The car is a ${car.make} ${car.model} from ${car.year}.`);
}
displayCarInfo(car);
Output

5. Create an object named book with properties title, author, and pages. Write a function isLongBook that takes a book object as a parameter and returns true if the book has more than 300 pages, otherwise false.
Here’s an example program:
let book = {
title: “The Great Gatsby”,
author: “F. Scott Fitzgerald”,
pages: 218
};
function isLongBook(book) {
return book.pages > 300;
}
console.log(isLongBook(book)); // Output: false
Output



