HTML
CSS
Bootstrap
JavaScript
C#
SQL
Salesforce Admin
Exercise
Study Material
✔ C# Tutorial
✔ C# Basic
✔ C# Control Statement
✔ C# Function
✔ C# Arrays
✔ C# Object Class
✔ C# Properties
✔ C# Inheritance
✔ C# Polymorphism
✔ C# Abstraction
✔ C# Namespace
✔ C# Exception Handling
✔ C# Collections
✔ C# Misc
Abstract Class in C#
In C#, abstract class is a class which is declared abstract. It can have abstract and non-abstract methods. It cannot be instantiated. Its implementation must be provided by derived classes. Here, derived class is forced to provide the implementation of all the abstract methods.
Abstract classes are the way to achieve abstraction in C#. Abstraction in C# is the process to hide the internal details and showing functionality only. Abstraction can be achieved by two ways:
1. Abstract class
2. Interface
Abstract class and interface both can have abstract methods which are necessary for abstraction.
A method which is declared abstract and has no body is called abstract method. It can be declared inside the abstract class only. Its implementation must be provided by derived classes.
For example:
public abstract class Shape
{
public abstract double Area { get; } // Abstract property (no implementation)
public abstract void Draw(); // Abstract method (no implementation)
}
public class Square : Shape
{
private double side;
public Square(double side)
{
this.side = side;
}
public override double Area { get { return side * side; } }
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine(“Drawing a square…”);
}
}
Example :
using System;
// Abstract class Vehicle
abstract class Vehicle
{
public string Model { get; set; }
public string Manufacturer { get; set; }
public int Year { get; set; }
// Abstract method to start the vehicle
public abstract void Start();
// Abstract method to stop the vehicle
public abstract void Stop();
// Abstract method to drive the vehicle
public abstract void Drive();
}
// Concrete subclass Car
class Car : Vehicle
{
public override void Start()
{
Console.WriteLine(“Car started.”);
}
public override void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine(“Car stopped.”);
}
public override void Drive()
{
Console.WriteLine(“Car is being driven.”);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Using the vehicles
Vehicle car = new Car();
car.Start();
car.Drive();
car.Stop();
}
}
Output: Car started.
Car is being driven.
Car stopped.
Practice
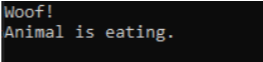
1.Define the Animal abstract class with an abstract method MakeSound() and a concrete method Eat() that outputs "Animal is eating." Then, define a Dog class that inherits from Animal and overrides the MakeSound() method to output "Woof!" In your application's entry point (e.g., Main method), instantiate a Dog object using an Animal reference (Animal myPet = new Dog();) due to polymorphism. Call myPet.MakeSound() to hear "Woof!" and myPet.Eat() to see "Animal is eating."
OUTPUT
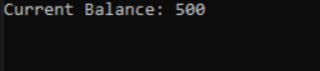
2.Define an abstract class BankAccount with properties and abstract methods representing common banking functionalities such as Deposit and Withdraw. Then, create a derived class SavingsAccount that inherits from BankAccount and implements the abstract methods (Deposit and Withdraw) with specific logic for savings accounts. In your application's entry point (e.g., Main method), instantiate a SavingsAccount object and assign it to a BankAccount reference (BankAccount account = new SavingsAccount();) to leverage polymorphism. Use this reference to call Deposit(1000) and Withdraw(500) on the account object, and then display thecurrent balance by accessing the Balance property.
OUTPUT