✔ C# Tutorial
✔ C# Basic
✔ C# Control Statement
✔ C# Function
✔ C# Arrays
✔ C# Object Class
✔ C# Properties
✔ C# Inheritance
✔ C# Polymorphism
✔ C# Abstraction
✔ C# Namespace
✔ C# Exception Handling
✔ C# Collections
✔ C# Misc
Collections
Container for Data:
Collections in C# are containers that allow you to store and manipulate groups of related data elements.
They provide a convenient way to work with multiple values of the same or different types.
// Example of an array, a simple collection
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Dynamic Size:
Collections often have dynamic sizes, allowing you to add or remove elements without specifying the size upfront.
// Example of a list, a dynamic collection
List<string> names = new List<string>();
names.Add(“Alice”);
names.Add(“Bob”);
Different Types of Collections:
C# provides a variety of collection types, including arrays, lists, dictionaries, queues, and more.
// Example of a dictionary, a key-value pair collection
Dictionary<string, int> ageMap = new Dictionary<string, int>();
ageMap[“Alice”] = 25;
ageMap[“Bob”] = 30;
Common Types of Collections
Arrays:
Arrays are fixed-size collections that can hold elements of the same type.
They are accessed by index.
int[] scores = { 90, 85, 92, 88, 95 };
int firstScore = scores[0]; // Accessing the first element
Lists:
Lists are dynamic collections that can grow or shrink in size.
They are part of the System.Collections.Generic namespace.
List<string> fruits = new List<string>();
fruits.Add(“Apple”);
fruits.Add(“Banana”);
Dictionaries:
Dictionaries are key-value pair collections, allowing you to associate values with unique keys.
They are also part of the System.Collections.Generic namespace.
Dictionary<string, double> prices = new Dictionary<string, double>();
prices[“Apple”] = 1.99;
prices[“Banana”] = 0.99;
Iterating Through Collections:
Use loops to iterate through elements in a collection.
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
foreach (int number in numbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
Adding and Removing Elements:
Collections often provide methods to add, remove, or manipulate elements.
List<string> colors = new List<string>();
colors.Add(“Red”);
colors.Add(“Green”);
colors.Remove(“Red”);
Accessing Dictionary Values:
Retrieve values from a dictionary using keys.
Dictionary<string, int> population = new Dictionary<string, int>();
int cityPopulation = population[“CityName”];
Choose the Right Collection Type:
Select the collection type that best fits your requirements (e.g., array for a fixed-size collection, list for a dynamic collection, dictionary for key-value pairs).
// Good: Using a list for a dynamic collection
List<int> dynamicNumbers = new List<int>();
// Avoid: Using an array when dynamic resizing is needed
int[] fixedNumbers = new int[10];
Use Generics for Type Safety:
Utilize generic collection types for type safety and better performance.
// Good: Using a generic list with specific types
List<string> names = new List<string>();
// Avoid: Using a non-generic list without type specification
ArrayList oldList = new ArrayList();
Practices Tasks
1. Create a list of string and add elements in it with name Alice, Bob and Charlie then use the foreach loop to show all values in console.

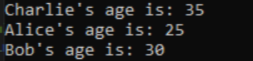
2. Create a dictionary with string keys Charlie, Bob and Alice and int values 35, 25 and 30, add element to the dictionary and show the value in console using keys.
3. Create a list of integers with the values 5, 2, 8, 1, 9 and then using sort method sort the value and using foreach loop show all values in console.