✔ C# Tutorial
✔ C# Basic
✔ C# Control Statement
✔ C# Function
✔ C# Arrays
✔ C# Object Class
✔ C# Properties
✔ C# Inheritance
✔ C# Polymorphism
✔ C# Abstraction
✔ C# Namespace
✔ C# Exception Handling
✔ C# Collections
✔ C# Misc
Arrays
In simple terms, an array is a collection of elements of the same type, identified by an index or a key. The index starts from zero, which means the first element is at index 0, the second at index 1, and so on.
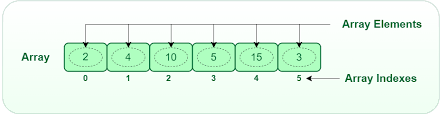
Array Declaratoin
int[] array1;
double[] array2;
bool[] array3;
int[] array1 = new int[5];
int[] array2 = new int[5]{4,5,1,7,3};
int[] array3 = {6,4,3,8,2};
Let's create a basic array to get a feel for it:
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Declare an array of integers
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Access and print elements using indexes
Console.WriteLine($”The third element: {numbers[2]}”);
}
}
Modifying Arrays
Arrays are not set in stone; you can modify their elements as needed. Let’s spice things up by changing a book title:
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Declare an array of strings
string[] books ;
books = new string[]{ “Harry Potter”, “Lord of the Rings”, “The Hobbit” };
// Modify an element
books[1] = “Game of Thrones”;
// Print the modified array
for (int i = 0; i < books.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($”Book {i + 1}: {books[i]}”);
}
}
}
In this example, we’ve changed the second element (index 1) from “Lord of the Rings” to “Game of Thrones.”
Multi-dimensional Arrays
What if your shelf isn’t just a straight line but a matrix with rows and columns? Enter multi-dimensional arrays!
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Declare a 2D array of integers
int[,] matrix = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} };
// Access and print elements
Console.WriteLine($”The element at row 1, column 2: {matrix[0, 1]}”);
}
}
In this example, we’ve created a 2D array (matrix) and accessed an element using both row and column indexes.


