Basic Structure of an HTML Document
The basic structure of an HTML Document is laid out below. It contains the essential building-block elements (i.e. doctype declaration, HTML, head, title, and body elements) upon which all web pages are created.
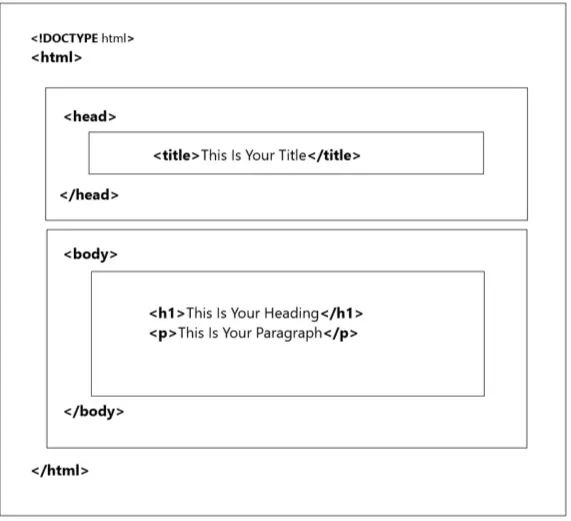
Now, let’s break down each part of this HTML structure:
| HTML Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <!DOCTYPE html> | Defines the document type and version of HTML (HTML5 in this case). |
| <html> | The root element of an HTML document that encapsulates all content. |
| <head> | Contains metadata about the document, such as the page title, character set, and links to external resources like CSS and scripts. |
| <title> | Sets the title of the web page, displayed in the browser’s title bar or tab. Also used by search engines for indexing and user experience. |
| <body> | Contains the visible content of the web page, including text, headings, images, links, and more. |
| <h1> to <h6> | Header elements used to define headings of varying levels. <h1> is the highest level and is typically used for the main page heading, while <h6> is the lowest. |
| <p> | Creates paragraphs of text, separating content into logical blocks for improved readability and organisation. |
Hello using HTML
To begin with HTML, here’s a simple “Hello HTML!”
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First HTML Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, HTML!</h1>
<p>This is my first HTML page.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
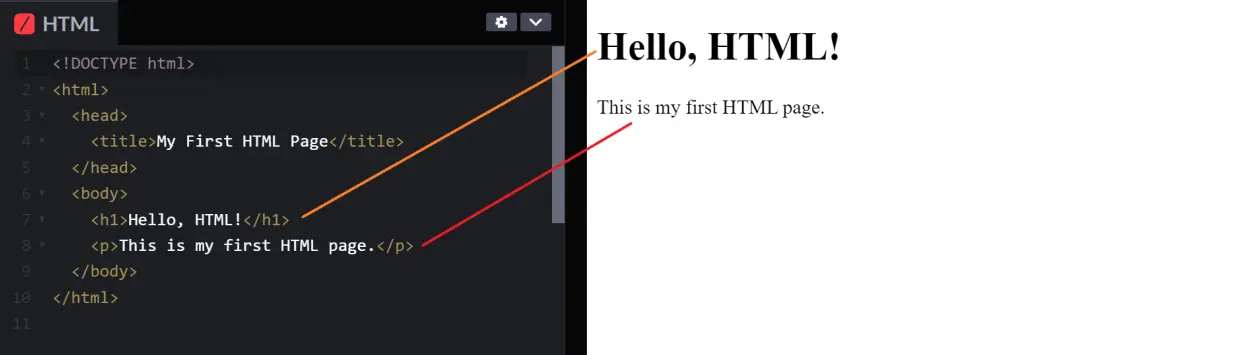
So, in essence, this HTML document is structured as follows:
1. The document starts with a declaration specifying it’s an HTML5 document.
2. Inside <html>, there are two main sections: <head> and <body>
3. The <head> section contains metadata like the page title.
4. The <body> section contains the visible content, including a main heading (<h1>) and a paragraph (<p>).
When you view this HTML document in a web browser, you’ll see the text “Hello, HTML!” displayed as the main heading and “This is my first HTML page.” as a paragraph, creating a basic web page.
How to View HTML Source
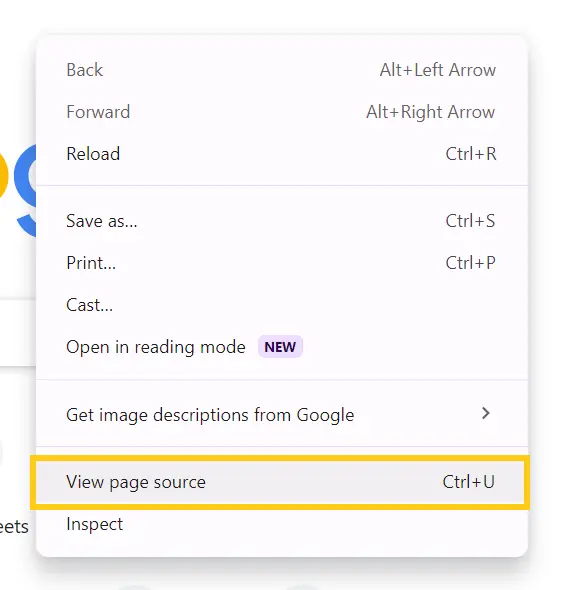
Viewing the HTML source code of a webpage can be quite insightful. Here’s how you can do it:
View HTML Source Code:
- On most web browsers, you can press CTRL + U while on an HTML page to open a new tab containing the HTML source code.

- Alternatively, right-click on the page and select View Page Sourcefrom the context menu. This will also open a new tab with the HTML source code displayed.
Inspect an HTML Element:
- If you’re curious about a specific element on a webpage, you can right-click on it (or on a blank area) and choose Inspectfrom the context menu.
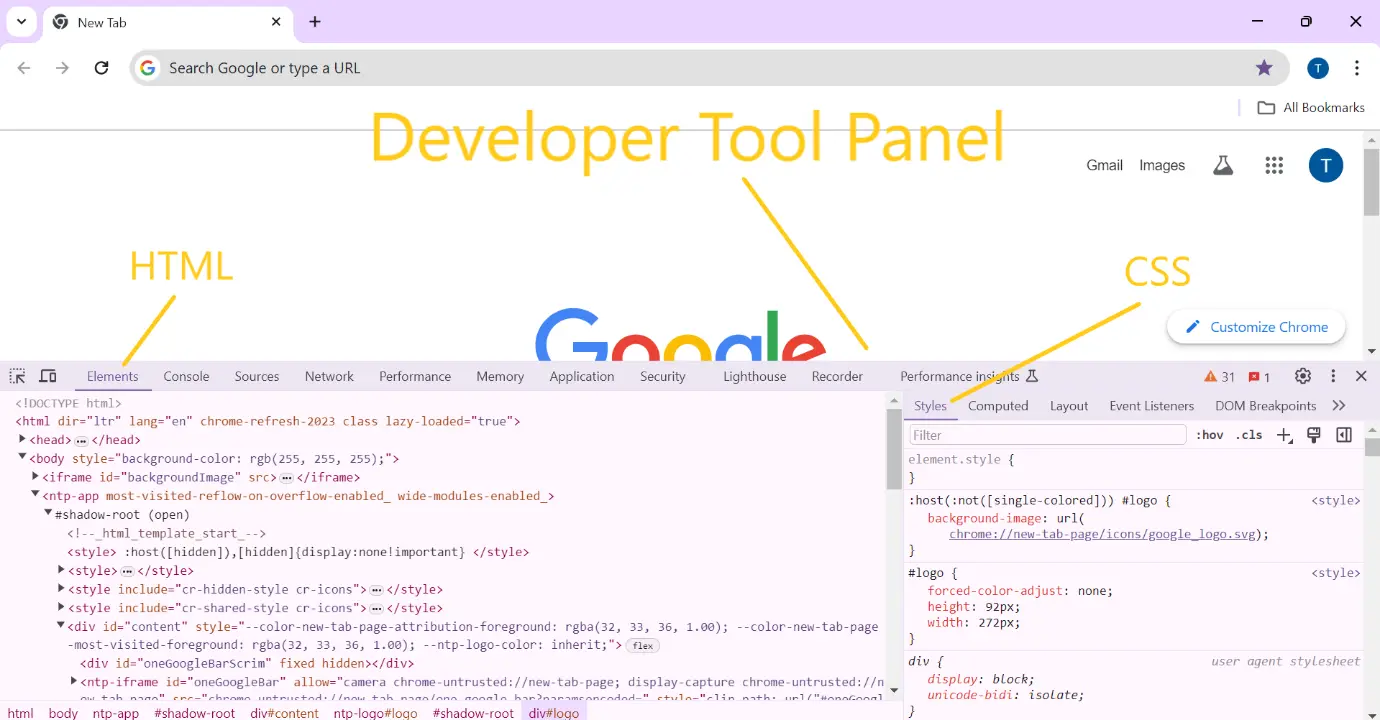
- This will open a developer tools panel where you can see the HTML structure of the page, including the selected element, along with any associated CSS styles.
- You can also edit the HTML or CSS directly within the developer tools panel, allowing you to experiment and see real-time changes to the webpage.
Course Video
Course Video In English
YouTube Reference :
It includes <!DOCTYPE html>, <html>, <head> for metadata, and <body> for visible content.
HTML is a markup language for creating web pages. Types include static HTML (basic pages) and dynamic HTML (interactive content).
It comprises a head for metadata and a body for webpage content.
A <header> defines introductory content like titles or navigation links.
Start with <!DOCTYPE html>, include <html>, and add structured content within <head> and <body> tags.
HTML uses tags enclosed in angle brackets, like <tag>Content</tag> for paired tags.
It typically includes a header, navigation, main content area, and footer.
Use structural tags like <header>, <nav>, <section>, and <footer>, styled with CSS.
Attributes are written as name=”value” within an opening tag, e.g., <img src=”image.jpg” alt=”text”>.
An HTML element includes an opening tag, optional content, and a closing tag, e.g., <p>Text</p>. For more, visit the Iqra Technology HTML Training page.


